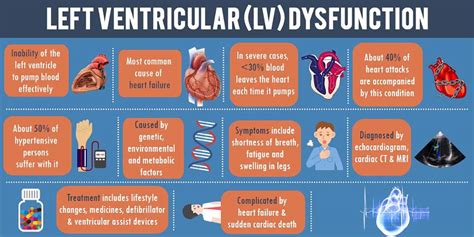
lv dysfunction Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common cause of left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure (ischemic cardiomyopathy [ICM]). The increasing sophistication of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous intervention (PCI) raises important questions about the appropriate role of revascularization, CABG, or PCI in treating patients .
8 000 2020
[email protected]. Īpašie piedāvājumi Akcijas periods: 14.05. - 20.05.2024. -52 % 1 19 € 2,49 € 2 49 € Arbūzi, 1 kg .
0 · what is severe lv impairment
1 · what is lv systolic dysfunction
2 · what does lv dysfunction mean
3 · lv dysfunction treatment
4 · lv dysfunction symptoms
5 · lv dysfunction grades
6 · life expectancy with diastolic dysfunction
7 · is 10 lv dysfunction
Cēsu iela 31 k-3 (6.ieeja), Rīga, LV-1012 iedzīvotājiem (67803300), veselības aprūpes profesionāļiem (67803301) [email protected] Lapas karte.
goyard tote green
Learn about the causes, symptoms, complications and treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy, a condition that thickens the walls of the lower left heart chamber. Find out how to prevent and manage this heart problem that . Stage A includes managing heart failure risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.This may include putting you on a thiazide diuretic or ACE inhibitor and a statin.; Stage B is diastolic dysfunction without .
Diastolic dysfunction is a problem with diastole, the first part of your heartbeat. Typically, your lower heart chambers relax and fill with blood during diastole. Normal LV diastolic function requires integration of left ventricular ejection, relaxation, and structure and is an active energy-requiring process. 1 For example, LV diastolic function becomes markedly abnormal immediately following coronary ligation, before detectable changes in other measures of cardiac function, including wall motion or electrocardiographic S . Left-sided heart failure. The heart's pumping action moves oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium, then on to the left ventricle, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common cause of left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure (ischemic cardiomyopathy [ICM]). The increasing sophistication of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous intervention (PCI) raises important questions about the appropriate role of revascularization, CABG, or PCI in treating patients .
sac ordinateur michael kors
Systolic heart failure is a specific type of heart failure that occurs in the heart’s left ventricle. The left and right ventricles are the bottom chambers of the heart.Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD) Management. Known Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. If no established diagnosis of heart failure, please see referral for suspected diagnosis of heart failure page Diastolic dysfunction is a heart condition that happens when there is a “stiffening” of the major pumping chambers of the organ (ventricles).This stiffness gets in the way of the heart’s ability to fill up with blood between heartbeats. Thank you for subscribing. You will receive the first heart failure and transplantation email in your inbox shortly. When seeking answers, people often look to experts for clear and accurate information.
Video: La fracción de eyección del corazón. What is “ejection fraction”? Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. Diastolic dysfunction is a chronic health condition that requires lifelong treatment and lifestyle changes. People with the condition can be at a higher risk of death from heart-related problems, but many people with diastolic dysfunction learn to manage the condition.
In systolic heart failure, the left ventricle becomes weak and can't contract and work the way it should. There's no cure, but you can make lifestyle changes to help treat it. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume). Stroke volume (SV) is calculated as the difference between end-diastolic volume . INTRODUCTION — . Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a clinical syndrome in which patients have signs and symptoms of HF as the result of high left ventricular (LV) filling pressure despite normal or near normal LV ejection fraction (LVEF; ≥50 percent) [].Most patients with HFpEF also display normal LV volumes and an abnormal . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which there is an increase in left ventricular mass, either due to an increase in wall thickness or due to left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both. Most commonly, the .
Central Illustration. Current Clinical Practice of Stage A to D HF Related to Cancer Therapeutics (Upper Panel) Key clinical developments (Clinical use [square], recognition of cancer treatment–related cardiotoxicity [star], and . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is when the heart’s main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, becomes thicker and less able to pump blood efficiently.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the ventricles along with impaired contractility defined as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 40%. By definition, patients have systolic dysfunction and may or may not have overt symptoms of heart failure. This disease process .
Prescriptions . Treating diastolic dysfunction can be a challenge. There are no medications that treat diastolic heart failure, with the possible exception of the diuretic drug spironolactone.That's why the best approach is to treat the underlying issues that are causing diastolic heart failure (e.g., smoking, hypertension, coronary disease, obesity, etc.).Ventricular dyssynchrony is a disorganized contraction of your heart’s lower chambers (ventricles). This doesn’t allow your heart to pump as well as it should. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. In response to this pressure overload, the inner walls of the heart may respond by getting thicker.Diastolic dysfunction and heart failure: Causes and treatment options
Ventricular failure manifests in many forms, its underlying physiology ranging from overt left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction to isolated right ventricular (RV) diastolic dysfunction, and the wide portfolio of resulting symptoms vary from chronic fluid retention to acute multiorgan dysfunction and death.Echocardiographicassessmentof left ventricular (LV) diastolic function is an integral part of theroutineevaluationofpatients presenting with symptoms of Diastolic heart failure occurs when signs and symptoms of heart failure are present but left ventricular systolic function is preserved (i.e., ejection fraction greater than 45 percent).
INTRODUCTION. Asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction (ALVSD) is defined as depressed LV systolic function in the absence of heart failure (HF) symptoms, which is called "stage B HF" in the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines []. (See "Approach to diagnosis of asymptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction", . RV dysfunction (RVD), defined here as evidence of abnormal RV structure or function, is associated with poor clinical outcomes independently of the underlying mechanism of disease: across the spectrum of left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) in patients with acute and chronic heart failure (HF), after cardiac surgery, acute myocardial infarction (MI), .
what is severe lv impairment
what is lv systolic dysfunction
what does lv dysfunction mean
All. Video. Community. Interior. 3D Tours. Experience the caliber of amenities and modern features we have to offer you at Evolve. View the gallery for a preview and call to schedule a tour!
lv dysfunction|what is lv systolic dysfunction